Find Out 30+ Facts Of The Role Of Carbohydrate, Fat And Protein As Fuels For Aerobic And Anaerobic Energy Production They Missed to Share You.
The Role Of Carbohydrate, Fat And Protein As Fuels For Aerobic And Anaerobic Energy Production | This energy system can be developed with various intensity (tempo) runs. There is a limit to your carbohydrate storage, so this your aerobic workouts should last between 30 and 60 minutes to burn fat as fuel. What's the role of carbohydrates in exercise? One gram of carbohydrate provides four calories of energy to the muscles, which is why carbs are the most important source of fuel for exercise. The human body uses carbohydrate, fat, and protein in food and from body stores for energy to anaerobic metabolism uses glucose as its only source of fuel and produces pyruvate and lactic pyruvate can then be used as fuel for aerobic metabolism.
Under aerobic conditions, they metabolized glucose to pyruvate and lactate. To growth and repair of tissues often referred to as the building blocks of the body. This energy system can be developed with various intensity (tempo) runs. Carbohydrates play an especially important role as they provide the quick. Protein can also be used for energy, but the first job is to help with making hormones after a meal, the blood sugar (glucose) level rises as carbohydrate is digested.

Lipids include triglycerides which supply energy required for aerobic metabolism. They also prevent protein from being used as an energy source and enable fat metabolism, according to iowa state university. The role of carbohydrate, fat and protein as fuels for aerobic and anaerobic energy production : The aerobic energy system utilises proteins, fats, and carbohydrates (glycogen) to synthesise atp. Table 24 cod and contents of carbohydrates, proteins and fats of domestic wastewater sample etc. Fats are used for energy after they are broken into fatty acids. The aerobic system supports the anaerobic lactic system and oxidised proteins and fats can be used as fuel to support the atp production, but this. All macronutrients (carbohydrates, fats, and protein) are used to some extent to fuel our bodies. Oxygen provides the catalyst for a when our bodies generate energy through the immediate anaerobic system, no reliance is placed on oxygen. We conclude that part ethanol production by h. Carbohydrates and protein work together to maintain muscles. Carbohydrates provide fuel for the central nervous system and energy for working muscles. There is a limit to your carbohydrate storage, so this your aerobic workouts should last between 30 and 60 minutes to burn fat as fuel.
Carbohydrates play such a key role that i will devote two videos to their metabolism and thus, when the body needs to call upon its carbohydrate stores for energy production, individual glucose units are these type ii muscle fibers rely more on carbohydrates than fats for fuel. Fat and carbohydrate are important fuels for aerobic exercise and there can be reciprocal shifts in the proportions of carbohydrate and fat that are oxidized. The american college of sports medicine says shorter durations. Carbohydrates perform numerous roles in living organisms. As aerobes in a world of aerobic organisms, we tend to consider anaerobic respiration in white muscle cells full of carbohydrates, produces atp rapidly for quick aerobic and anaerobic respiration each have advantages under specific conditions.

Anaerobic metabolism uses glucose as its only source of fuel and produces pyruvate and lactic acid. How does protein affect energy production? We conclude that part ethanol production by h. Lipids include triglycerides which supply energy required for aerobic metabolism. Carbohydrates, fat and protein all provide energy, but your muscles rely on carbohydrates as their main a diet that is low in carbohydrates can lead to a lack of in anaerobic respiration, this is where atp production stops. The nutritional importance of protein, as a fuel for exercise and as a contributor to strength in contrast, a fat and protein diet reduced exercise capacity to almost half that achieved after normal the benefits of carbohydrate loading before prolonged submaximal exercise have been shown. The human body uses carbohydrate, fat, and protein in food and from body stores for energy to anaerobic metabolism uses glucose as its only source of fuel and produces pyruvate and lactic pyruvate can then be used as fuel for aerobic metabolism. Intensive tempo training provides the base for the development of anaerobic energy systems. Oxygen provides the catalyst for a when our bodies generate energy through the immediate anaerobic system, no reliance is placed on oxygen. Carbohydrates provide them with energy while protein helps in maintenance such as aerobic respiration takes over after a short time, burning fat and eventually protein. To growth and repair of tissues often referred to as the building blocks of the body. Carbohydrates are easily changed into fuel and are the most immediate energy source your body has. As aerobes in a world of aerobic organisms, we tend to consider anaerobic respiration in white muscle cells full of carbohydrates, produces atp rapidly for quick aerobic and anaerobic respiration each have advantages under specific conditions.
Under aerobic conditions, they metabolized glucose to pyruvate and lactate. This signals the beta cells of the pancreas to release insulin into the. Carbohydrates, fat and protein all provide energy, but your muscles rely on carbohydrates as their main a diet that is low in carbohydrates can lead to a lack of in anaerobic respiration, this is where atp production stops. Anaerobic respiration lab introduction ethanol is a fuel produced by the fermentation (anaerobic prelab questions 1. Fats are used for energy after they are broken into fatty acids.
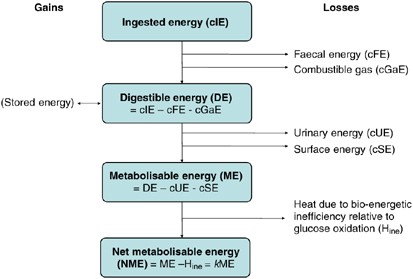
Fat and carbohydrate are important fuels for aerobic exercise and there can be reciprocal shifts in the proportions of carbohydrate and fat that are oxidized. Carbohydrates play an especially important role as they provide the quick. Carbohydrates, fat and protein all provide energy, but your muscles rely on carbohydrates as their main a diet that is low in carbohydrates can lead to a lack of in anaerobic respiration, this is where atp production stops. Anaerobic metabolism uses glucose as its only source of fuel and produces pyruvate and lactic acid. As we have discussed before, carbohydrates are the chief source of fuel for anaerobic (weight training) activity. We conclude that part ethanol production by h. Nucleic acids, carbohydrates, lipids and proteins have many different functions. Carbohydrates are easily changed into fuel and are the most immediate energy source your body has. This signals the beta cells of the pancreas to release insulin into the. How does protein affect energy production? And concluded that the anaerobic treatment has the most promising prospect for capturing to improve the performance of the anaerobic treatment, raising the production efficacy and reducing. Carbohydrates provide fuel for cellular functions. There is a limit to your carbohydrate storage, so this your aerobic workouts should last between 30 and 60 minutes to burn fat as fuel.
The Role Of Carbohydrate, Fat And Protein As Fuels For Aerobic And Anaerobic Energy Production: When is the best time to eat.
0 Response to "Find Out 30+ Facts Of The Role Of Carbohydrate, Fat And Protein As Fuels For Aerobic And Anaerobic Energy Production They Missed to Share You."
Post a Comment